Machining of cemented carbide with diamond coated micro ball nose end mills
 Jul 14, 2020|
Jul 14, 2020| View:1337
View:1337Machining of cemented carbide with diamond coated micro ball nose end mills
With the right tools and machine tools, milling hard materials such as HRC60 hardness of the D-2 tool steel is not difficult. However, it is not so easy to mill harder materials, such as hard alloys. These materials are usually available only by grinding or Electrical discharge machining.
With the introduction of Union Tool Inc.'s UDCB series micro ball nose end mills, much has changed. "Makino believes the development of this tool is important, perhaps as important as the introduction of hard milling in the mid-1990s, " says John Bradford, head of microfabrication research and development at Makino, in the past, the success rate of milling hard alloy workpiece with hard alloy cutter was only 10%-20% .
At IMTS 2012, Muye District demonstrated the use of UDCB with a diameter of 1 mm for rough milling and fine milling of cemented carbide punches with a micro ball nose end mills with a hardness of at least HRA93 at its IQ300 micromachining center (figures 1 and 2) . After 38 minutes of machining, the tool wear was only 1.8 m. If the workpiece is Electrical discharge machining, it takes at least four hours (including electrode programming, machining the electrode, and electrical discharge machining the workpiece) . "You need to process at least three copper-tungsten electrodes. In most cases, you have to process four electrodes if you want to maintain accuracy of 5M or better, " Bradford said

Fig. 1udcb diamond coated micro ball nose end mills

Fig. 2 carbide punches
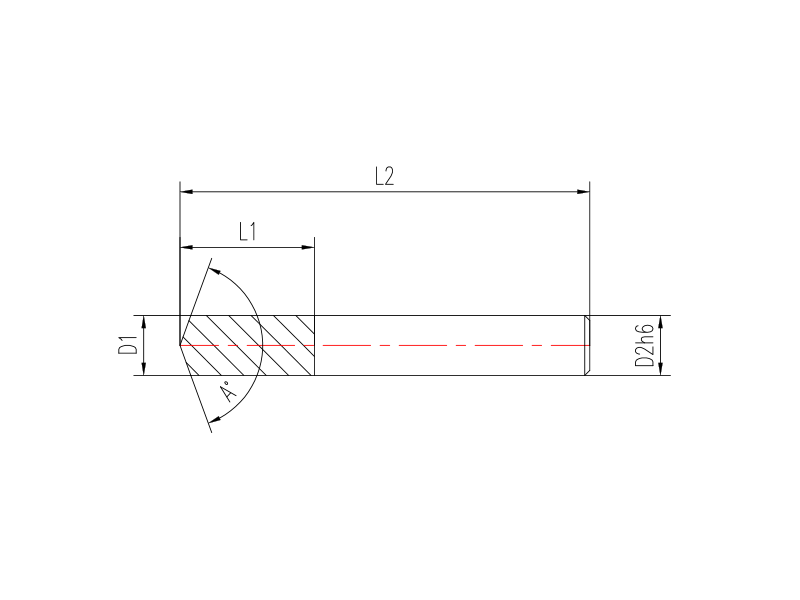
In order to milling multiple workpiece with depth of 2.200 mm, the spindle speed of 30,000 r/min and the feed speed of 300 mm/min were used for Udcb double-edged micro ball nose end mills, and the chip load per blade was 10 m. The micro ball nose end mills was clamped on MST Uno hot-loading tool chuck, and the maximum diameter jump error of the factory certification was 600nm.
The diameter of the Udcb double-edged micro ball nose end mills developed by the joint tool company is 0.2-6 mm. According to Jonathan Hay, the company's Senior Vice President of sales and marketing, diamond coatings deposited by hot filament CVD with a thickness of more than 10 m provide good durability under precisely controlled processing conditions, and minimize the corner radius effect. Compared with plasma CVD, hot-filament CVD can deposit more uniform coatings on the surface of complex shape.
The hardness of diamond coating on UDCB micro ball nose end mills is about 100GPa (9,000HV) , which is very close to that of single crystal diamond. In addition, through precise interface control, the adhesion between diamond coating and substrate is very strong.
Because the cutting force of milling hard alloy is about 2 times larger than that of milling D-2 tool steel (HRC60) , in order to minimize the vibration, it is necessary to use high rigidity machine tool when using UDCB micro ball nose end mills, and gradually cut into the workpiece with a spiral feed tool. During the machining demonstration at the IMTS trade show, Makino used a 1° spiral angle and reduced the feed rate by 90% when the milling cutter cut into the workpiece.
"We find that the Auger feed is more reliable because the cutting force is more uniform, " says Hay, noting that the feed can be kept constant throughout the cutting process. The UDCB micro ball nose end mills uses a standard spiral groove to enhance the rigidity of the tool. Uniform and uniform cutting forces help to avoid damage to highly brittle parts, tool substrates, and coatings.
Muino uses blow-dry air to remove chips and cool the tool/workpiece interface during a machining demonstration. Hay says the method is superior to spray cooling with water-based cutting fluid and oil mist cooling. "If it is cooled by oil mist, it may form a small oil and lump containing cemented carbide chips. The continuous blowing of air is more reliable and environmentally friendly. "
As mentioned above, although hard alloy dies and other workpieces of similar hardness may be machined by grinding, however, the types of features (especially the micro-features) that can be machined are limited by the ability of the diamond wheel to reach or enter the features. While other ultra-hard tools such as the PCBN and PCD tools are available, these tools can cost up to four times as much as the UDCB micro ball nose end mills ($534.50-$674.50 depending on the diameter) , and these cutting tools in the processing basically will not wear out gradually. "PCBN is very difficult to make into a tool, " says Hay. "PCD materials lack anisotropy (anisotropic materials have different properties measured in different directions) , so they tend to break down. "
Bradford said he was somewhat surprised by the reaction of the visitors during the demonstration, "They can't believe what they're seeing. Makers of cemented carbide tools are going to have new tools. It's a historic technological advance. "